Temomide
(Temozolomide)
Composition:
Each capsule contains 20mg Temozolomide
Each capsule contains 100mg Temozolomide
Each capsule contains 250mg Temozolomide
ATC Code
L01AX03- Temozolomide
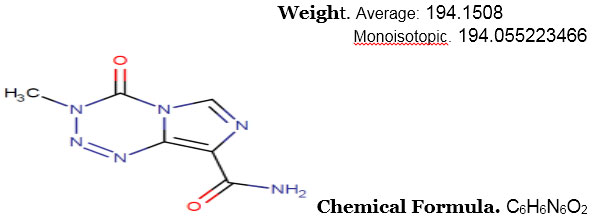
Structure
Description
Temozolomide is an orally administrated alkylating agent used largely in the therapy of malignant brain tumors including glioblastoma and astrocytoma. Temozolomide has been associated with a low rate of serum enzyme elevations during treatment and with rare instances of clinically apparent cholestatic liver injury.
Indication
- Glioblastoma Multiforme (GBM)
- Anaplastic Astrocytoma
Associated Conditions
- Advanced Metastatic Melanoma
- Newly diagnosed high grade glioma
- Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
- Neuroblastoma
Pharmacodynamics
Temozolomide is a prodrug of the imidazotetrazine class that requires nonenzymatic hydrolysis at physiological pH in vivo to perform alkylation of adenine/guanine residues, leading to DNA damage through futile repair cycles and eventual cell death. Temozolomide treatment is associated with myelosuppression, which is likely to be more severe in females and geriatric patients. Patients must have an ANC of ≥1.5 x 109/L and a platelet count of ≥100 x 109/L before starting therapy and must be monitored weekly during the concomitant radiotherapy phase, on days one and 22 of maintenance cycles, and weekly at any point where the ANC/platelet count falls below the specified values until recovery. Cases of myelodysplastic syndrome and secondary malignancies, including myeloid leukemia, have been observed following temozolomide administration. Pneumocystis pneumonia may occur in patients undergoing treatment, and prophylaxis should be provided for patients in the concomitant phase of therapy with monitoring at all stages. Severe hepatotoxicity has also been reported, and liver testing should be performed at baseline, midway through the first cycle, before each subsequent cycle, and approximately two to four weeks after the last dose. Animal studies suggest that temozolomide has significant embryo-fetal toxicity; male and female patients should practice contraception up to three and six months following the last dose of temozolomide, respectively
Mechanism of Action
Imidazotetrazine derivative prodrug; active metabolite MTIC methylates guanine-rich areas of DNA that initiate transcription, which lead to DNA double strand breaks and apoptosis
Product Information
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
