Cesna
(Mesna Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulphonate)
Composition:
Each injection contains Mesna Sodium 2-mercaptoethanesulphonate 400mg
ATC Code
V03AF01 — Mesna
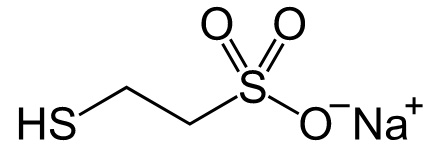
Structure
Description
Mesna is a detoxifying agent to inhibit the hemorrhagic cystitis induced by ifosfamide. This medication is used to reduce the risk of bleeding in the bladder (hemorrhagic cystitis), which is a very serious side effect of treatment with a cancer chemotherapy drug called ifosfamide. Mesna helps to protect the lining of the bladder against damage from ifosfamide. The body breaks down ifosfamide to form a product that can harm the bladder, and mesna works by making this product less harmful. However, mesna does not change ifosfamide’s anti-cancer effects.
Indication
- Mesna is used in the treatment of ovarian cancer, blood cancer, hemorrhagic cystitis and methotrexate toxicity.
Pharmacodynamics
Distribution
0.65 ± 0.24 L/kg; distributed to total body water.
Metabolism
Rapidly oxidized to mesna disulfide (dimesna) in the intravascular compartment. Mesna and dimesna do not undergo hepatic metabolism.
Excretion
Urine (32% as mesna; 33% as dimesna).
Time to Peak
Plasma: Oral: Free mesna: 1.5 to 4 hours; Total mesna: 3 to 7 hours.
Half-Life Elimination
Mesna: ~22 minutes; Dimesna: ~70 minutes.
Protein Binding
69% to 75%.
Mechanism of Action
Mesna belongs to abdominal pain a class of drugs called cytoprotectants. It protects the urinary bladder from harmful effects of ifosfamide and cyclophosphamide.
In blood, mesna is oxidized to dimesna which in turn is reduced in the kidney back to mesna, supplying a free thiol group which binds to and inactivates acrolein, the urotoxic metabolite of ifosfamide and cyclophosphamide